Led by the Polacek group, researchers looked into the roles in cancer of one of the four human noncoding vault RNAs, vault RNA 1-2. They found in human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines that vault RNA 1-2 contributes to several hallmarks of cancer cells. Also, through TCGA data they could show an association between the methylation of vault RNA 1-2's promoter and the patients' clinical conditions, pointing further at an oncogenic role of this vault RNA. Thus, vault RNA 1-2 could serve as a potential therapeutic target. Regarding biological findings, the comparison with results gained on vault RNA 1-1 showed clear distinctions further underlining the notion that each of the four vault RNAs has its distinctive roles. Their findings have been published in NAR Cancer.
Abstract
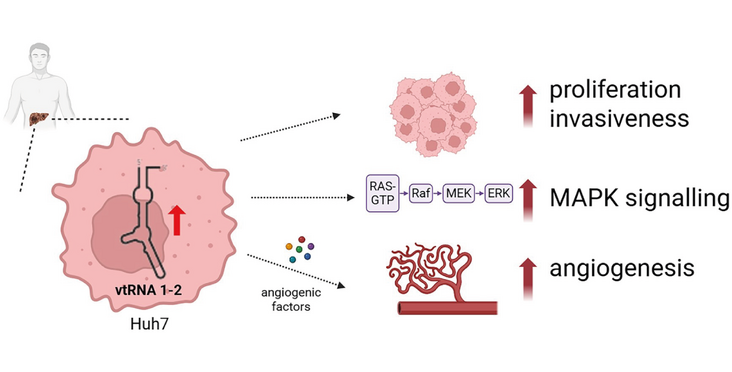
Noncoding RNAs play pivotal roles in tumorigenesis and cancer progression. Recent evidence has identified vault RNAs (vtRNAs) as critical regulators of cellular homeostasis. The human genome encodes four vtRNA paralogs, which are differentially expressed in cancer tissues and contribute to tumor development. The best studied vtRNA1-1 is involved in regulating apoptosis resistance, autophagy, lysosomal biogenesis, and drug resistance. Here, we present the first comprehensive characterization of vtRNA1-2 using a knockout hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell line. Loss of vtRNA1-2 impaired cancer cell viability and proliferation by modulating mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling. Additionally, vtRNA1-2-deficient cells exhibited reduced motility and a decreased invasive potential. Unlike vtRNA1-1, vtRNA1-2 did not influence autophagy or lysosomal activity. Instead, vtRNA1-2 is implicated in the regulation of angiogenesis, a key process in tumor progression. VTRNA1-2-promoter hypomethylation is correlated with chromatin accessibility in liver cancer samples and we uncovered an association between promoter methylation and key patient clinical conditions as registered in the TCGA metadata. These findings highlight a distinct oncogenic role for vtRNA1-2 in HCC and suggest that it may serve as a potential therapeutic target. Our study underscores the functional divergence among vtRNA paralogs, supporting the concept that each exerts unique biological effects rather than acting as redundant molecular entities.
Read the Publication in NAR Cancer (Open Access)
Abstract and figure from Gallo, Suspitsyna, et al (2025) NAR Cancer published under a CC BY 4.0 license.